Comprehensive Guide to Maize Weevil Control and Its Importance
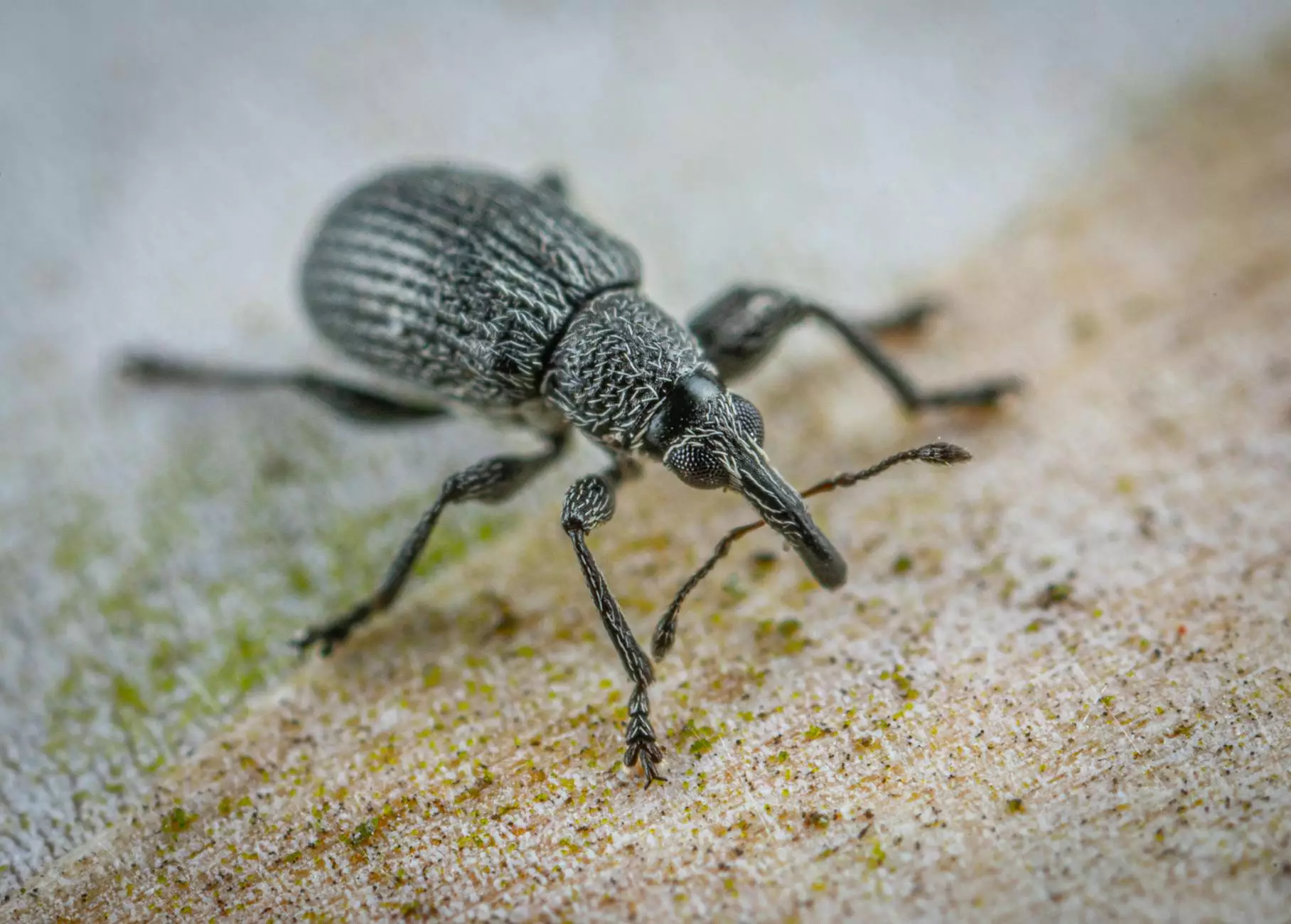

Maize weevils are notorious pests that significantly threaten the quality and yield of maize crops globally. Effective maize weevil control is essential for farmers looking to optimize their production and maintain the quality of their harvest. This article seeks to provide comprehensive insights into the biology of maize weevils, the damage they cause, and effective control measures that can be implemented to mitigate their impact.
Understanding the Maize Weevil: Biology and Habitats
The maize weevil, or Sitophilus zeamais, is a small beetle belonging to the family Curculionidae. Adults are approximately 2.5 to 5 mm in length and have a distinctive elongated snout. The lifecycle of the maize weevil can be summarized as follows:
- Egg Stage: Females lay eggs inside whole maize grains. One female can lay up to 400 eggs in her lifetime.
- Lava Stage: Upon hatching, the larvae burrow into the grain, feeding on the endosperm.
- Pupal Stage: After about two weeks, the larvae pupate, emerging as adult weevils within 20 days.
Understanding this lifecycle is crucial for implementing effective maize weevil control measures, as each stage requires different management strategies.
Impact of Maize Weevils on Crop Production
Maize weevils pose significant risks to maize quality and yield. The damage caused by these pests can be categorized into two primary areas:
1. Quality Degradation
Invasion by maize weevils leads to:
- Reduced Nutritional Value: Infestation leads to the destruction of the grain’s interior, significantly lowering its nutritional content.
- Unpleasant Odors and Tastes: Infested grains often develop off-flavors that make them unappealing for consumption.
2. Economic Losses
The economic repercussions of maize weevil infestations are stark:
- Decreased Market Value: Infested maize fetches lower prices in the market.
- Increased Storage Costs: Frequent treatments and monitoring increase operational costs for farmers.
Effective Maize Weevil Control Strategies
Implementing robust maize weevil control strategies can significantly mitigate losses associated with this pest. Here are several proven methods:
1. Preventive Measures
Taking steps to prevent infestations before they occur is the most cost-effective approach. Key preventive measures include:
- Proper Storage Conditions: Store maize in cool, dry areas with low humidity to inhibit weevil growth.
- Regular Monitoring: Check stored grains frequently for signs of infestation and act quickly when detected.
- Use of Clean Seed: Always ensure that seeds are free from pests before planting.
2. Biological Control Methods
Biological pest control methods utilize natural predators or pathogens to manage weevil populations:
- Beneficial Insects: Introducing parasitoids that naturally prey on maize weevils can help keep their numbers in check.
- Neem Extracts: Neem oil and other organic compounds can act as natural insecticides, reducing pest populations without harming beneficial insects.
3. Mechanical Control Techniques
Mechanical control involves physical methods of managing pest infestations:
- Traps: Use of pheromone traps can help monitor and reduce weevil populations in storage areas.
- Heat Treatment: Exposing grains to high temperatures can kill all life stages of the maize weevil.
4. Chemical Control Solutions
In cases of severe infestations, chemical control measures may be needed:
- Insecticides: Applying approved insecticides can help eliminate weevil populations, but should be done with caution to minimize harm to non-target species.
- Fumigation: For large-scale infestation, fumigation is a highly effective method of controlling weevils in stored grains.
Integrating Practices for Maximum Control
The most effective maize weevil control involves integrating various practices into a comprehensive management plan. This can include:
- Combining Biological and Chemical Controls: Using a mix of both approaches can provide optimal control while reducing the reliance on chemical treatments.
- Farmer Education: Training farmers on pest identification and management enhances community resilience against maize weevil infestations.
- Research and Development: Continued innovation in pest management practices and studies on maize weevil biology can lead to better control strategies.
The Role of Technology in Maize Weevil Control
Advancements in technology play a crucial role in modern pest management. Tools such as:
- Smart Traps: Using traps equipped with monitoring systems can alert farmers in real-time about pest activity.
- Data Analytics: Collecting data on pest populations can help refine control strategies, leading to more effective management practices.
In conclusion, effective maize weevil control is essential for maintaining high-quality maize production and safeguarding the economic interests of farmers. By understanding the biology of the pest, implementing preventive measures, utilizing both biological and mechanical control techniques, and embracing technological advancements, farmers can significantly reduce the impact of this pest on their crops.
Continuously educating oneself and staying informed about the latest advancements in pest management will empower farmers to tackle maize weevil challenges head-on, ensuring a prosperous farming future.
Ultimately, the goal of maize weevil control is not just about protecting crops but also about securing food sources for communities around the world. As we continue to develop better practices and strategies, the fight against maize weevils will pave the way for healthier, more resilient agricultural systems.